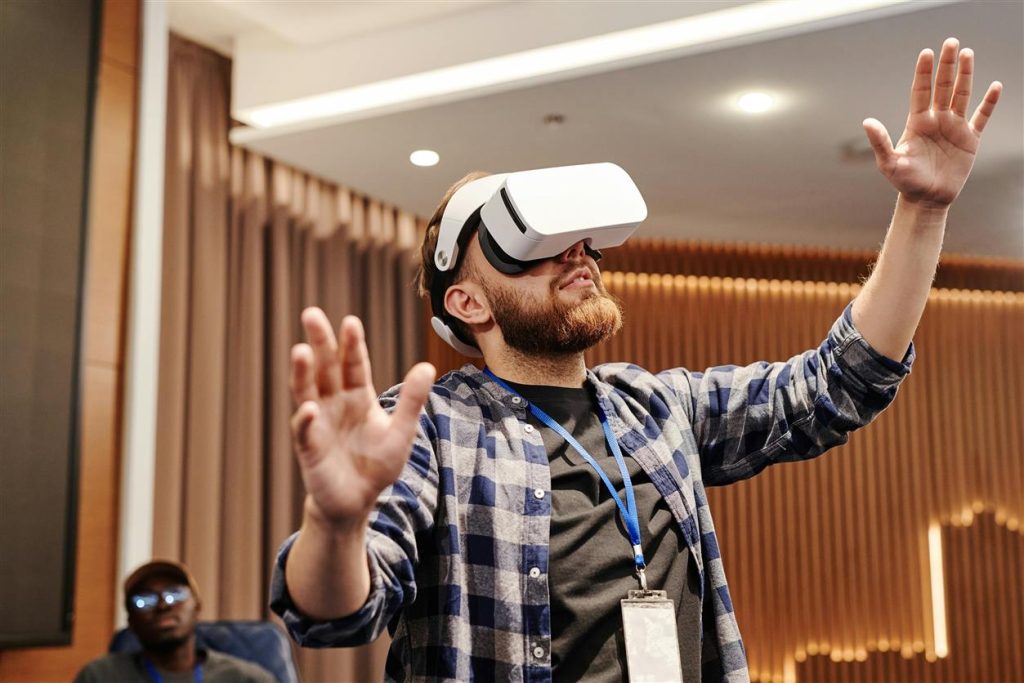
The term “metaverse” has transitioned from a concept in science fiction to a tangible and rapidly evolving facet of digital reality. As we move further into the 2020s, the metaverse is emerging as a significant technological and cultural development, promising to reshape the way we interact with digital environments. This essay explores the metaverse in depth, examining its definition, current state, technological underpinnings, potential applications, and the challenges and implications it presents.
Understanding the Metaverse
Definition and Concept
The metaverse is often described as a collective virtual shared space that is created by the convergence of virtually enhanced physical reality and physically persistent virtual reality. This concept extends beyond traditional virtual worlds by aiming to create a comprehensive and immersive digital environment where users can interact with each other and digital objects in real-time. The term was first popularized by Neal Stephenson’s 1992 science fiction novel, “Snow Crash,” and has since evolved to encompass a broader vision of interconnected digital experiences.
Key Characteristics
- Persistent and Real-Time: The metaverse is designed to be persistent, meaning it continues to exist and evolve even when users are not actively participating. Real-time interactions enable users to engage with the environment and each other seamlessly.
- Interoperability: A defining feature of the metaverse is its potential for interoperability, allowing users to move between different virtual spaces and applications while retaining their digital identity and assets.
- Immersive Experience: The metaverse aims to provide an immersive experience through technologies such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR). These technologies blend digital and physical worlds, creating a more engaging and interactive experience.
Technological Foundations
Virtual Reality (VR)
Virtual Reality (VR) is a core technology enabling the metaverse. VR creates a fully immersive digital environment where users can interact with 3D spaces and objects using VR headsets and controllers. Recent advancements in VR technology have led to higher resolution displays, more accurate motion tracking, and improved haptic feedback, enhancing the overall immersive experience.
- Hardware Innovations: Modern VR headsets are becoming lighter, more comfortable, and more affordable. Advances in haptic feedback technology allow users to feel virtual objects and textures, adding a layer of realism to the experience.
- Software Development: VR platforms and applications are evolving to provide more sophisticated and interactive experiences. From virtual meetings and social interactions to gaming and education, VR is being integrated into various aspects of the metaverse.
Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital information onto the physical world, creating an enhanced version of reality. AR technology is used to superimpose digital elements, such as text, images, and animations, onto real-world objects.
- AR Devices: Devices such as AR glasses and smartphone applications are enabling users to interact with digital content in their physical environment. These devices are becoming more advanced, with improved display quality and gesture recognition.
- Applications: AR applications range from interactive marketing and gaming to educational tools and navigation aids. In the context of the metaverse, AR contributes to blending digital and physical realities, allowing users to experience digital content in real-world settings.
Mixed Reality (MR)
Mixed Reality (MR) combines elements of both VR and AR, creating a hybrid experience where digital and physical worlds coexist and interact. MR technology allows users to manipulate and interact with virtual objects as if they were part of the physical environment.
- MR Devices: Devices such as Microsoft’s HoloLens and Magic Leap are examples of mixed reality hardware that facilitate this integration. These devices enable users to see and interact with digital content in their physical surroundings.
- Use Cases: MR has applications in various fields, including design, training, and collaboration. In the metaverse, MR enhances the immersive experience by allowing users to engage with both digital and physical elements simultaneously.
Applications of the Metaverse
Social Interaction
The metaverse is transforming social interaction by providing new ways for people to connect and engage with each other:
- Virtual Social Spaces: Platforms like Meta’s Horizon Workrooms and VRChat offer virtual social spaces where users can meet, chat, and collaborate. These spaces simulate real-world social interactions, enabling users to form communities and relationships in a digital environment.
- Events and Gatherings: The metaverse is becoming a venue for virtual events, such as concerts, conferences, and social gatherings. These events allow participants to experience and interact with content in ways that traditional physical events cannot match.
Gaming and Entertainment
The gaming industry is a significant driver of metaverse development, with virtual worlds and gaming environments serving as foundational elements:
- Immersive Gaming: Metaverse platforms offer expansive virtual worlds where players can explore, compete, and collaborate. Games like “Fortnite” and “Roblox” have already demonstrated the potential of virtual worlds for social interaction and creative expression.
- Entertainment Experiences: Beyond gaming, the metaverse is creating new forms of entertainment, such as virtual concerts and interactive storytelling. These experiences leverage the immersive capabilities of VR and AR to engage audiences in novel ways.
Education and Training
The metaverse has the potential to revolutionize education and training by providing immersive and interactive learning environments:
- Virtual Classrooms: Educational institutions are exploring virtual classrooms where students can attend lectures, participate in discussions, and collaborate on projects in a digital setting. This approach offers flexibility and access to educational resources from anywhere in the world.
- Simulations and Training: The metaverse enables the creation of realistic simulations for training purposes, such as medical procedures, emergency response, and technical skills. These simulations provide hands-on experience and practical knowledge in a controlled environment.
Commerce and Economy
The metaverse is also shaping the future of commerce and economic activities:
- Virtual Shopping: E-commerce platforms are developing virtual stores where users can browse and purchase products in a digital environment. Virtual shopping experiences provide an immersive way to explore products and make purchasing decisions.
- Digital Economy: The metaverse is giving rise to a digital economy, where virtual goods and services are bought and sold. This includes digital assets such as virtual real estate, NFTs (non-fungible tokens), and in-game items, contributing to new economic opportunities and business models.
Challenges and Implications
Privacy and Security
As the metaverse expands, concerns about privacy and security become increasingly important:
- Data Protection: The collection and use of personal data within the metaverse raise privacy concerns. Ensuring that user data is protected and used responsibly is crucial to maintaining trust and security in digital environments.
- Cybersecurity: The metaverse is vulnerable to cybersecurity threats, including hacking, data breaches, and identity theft. Robust security measures and protocols are necessary to safeguard user information and prevent malicious activities.
Digital Divide
The metaverse has the potential to exacerbate the digital divide by creating disparities in access to technology and digital experiences:
- Access to Technology: High-quality VR and AR experiences require advanced hardware and high-speed internet, which may not be accessible to all individuals. Ensuring equitable access to metaverse technologies is essential to prevent exclusion and inequality.
- Economic Disparities: The digital economy within the metaverse may favor those with resources and technological skills, potentially widening economic disparities. Addressing these issues requires initiatives to promote digital literacy and access to technology.
Ethical Considerations
The development and use of the metaverse raise various ethical considerations:
- Digital Identity and Representation: The metaverse allows users to create and manage digital identities, which can impact self-perception and social interactions. Ethical considerations include the representation and management of digital personas and avatars.
- Content Moderation: Managing content and interactions within the metaverse presents challenges related to moderation and enforcement of community standards. Ensuring a safe and respectful environment requires effective moderation strategies and policies.
The Future of the Metaverse
The future of the metaverse holds immense potential for innovation and transformation:
- Integration of Emerging Technologies: The metaverse is likely to integrate with emerging technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT). These integrations will enhance the capabilities and experiences within the metaverse.
- Expanding Applications: As the metaverse evolves, its applications will expand to new areas, including healthcare, real estate, and environmental sustainability. The continued development of metaverse technologies will drive new opportunities and use cases.
- Cultural and Social Impact: The metaverse will shape cultural and social dynamics, influencing how people interact, collaborate, and engage with digital content. Its impact will extend to various aspects of daily life, from work and education to entertainment and socialization.

The metaverse represents a transformative frontier in digital reality, offering new possibilities for interaction, creativity, and economic activity. With advancements in VR, AR, and MR technologies, the metaverse is becoming an increasingly immersive and interconnected environment. As we navigate this new digital landscape, it is essential to address the challenges and implications associated with its development, including privacy, security, and ethical considerations.
The future of the metaverse holds great promise, with the potential to revolutionize various aspects of our lives and create new opportunities for innovation and growth. By understanding the current state and future potential of the metaverse, we can better prepare for the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead, shaping a digital reality that is inclusive, secure, and transformative.